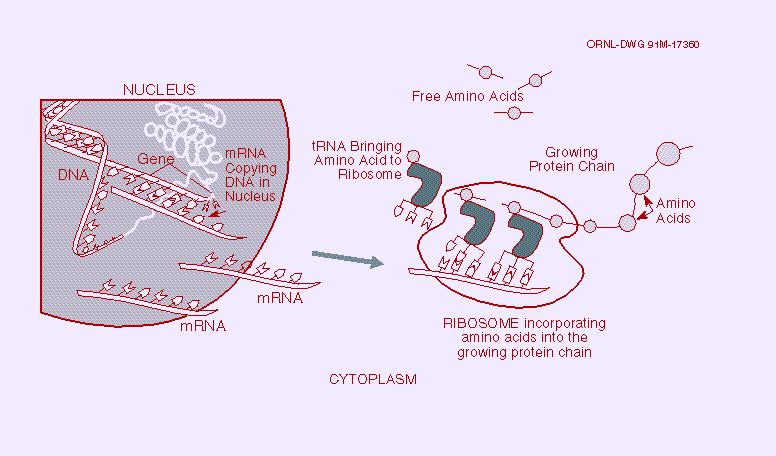
Fig. 5. Gene Expression.When genes are expressed, the genetic information (base sequence) on DNA is first transcribed (copied) to a molecule of messenger RNA in a process similar to DNA replication. The mRNA molecules then leave the cell nucleus and enter the cytoplasm, where triplets of bases (codons) forming the genetic code specify the particular amino acids that make up an individual protein. This process, called translation, is accomplished by ribosomes (cellular components composed of proteins and another class of RNA) that read the genetic code from the mRNA, and transfer RNAs (tRNAs) that transport amino acids to the ribosomes for attachment to the growing protein. (Source: see Fig. 4.)